Electric ball valve model preparation/code name designation method
Electric ball valve model preparation/code name designation method in China.
As an important equipment in the industrial automation control system, the electric ball valve has been used more and more in recent years due to its simple structure and convenient operation. It can not only be used to cut off or connect the medium in the pipeline, but also can be used for fluid Regulation and control! But because of the different working conditions of the pipeline, the electric ball valve models used are all different! The user should have a detailed understanding and cognition of the method of preparing the electric ball valve model!
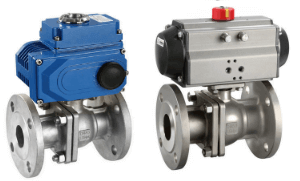
Pneumatic electric high platform ball valve
This electric ball valve model editing method includes the addition of additional conditions for the ball valve, the selection of the drive mode, the different connection form, the change of the structure form, the type of sealing material, the level of the valve pressure and the valve body material, etc.!
Electric ball valve model representation method:
Ball valve additional code:
V means the spool has a V-shaped structure, D means low temperature, B means heat preservation, P means eccentric structure, U, S and DY mostly mean top-mounted type;
Ball valve name code: Q means ball valve; Ball valve drive code: 2 means electro-hydraulic, 3 means turbine, 6 means pneumatic, 7 means hydraulic, 9 means electric, manual without code;
Code of connection method: 1 means internal thread, 4 means flange type, 6 means welding, 7 means wafer type;
Structure type code:
Floating type: 1 means straight flow channel, 2 means Y-type tee, 4 means L-type tee, 5 means T-type tee;
Fixed: 0 means hemispherical straight through, 6 means four-way flow channel, 7 means straight flow to, 8 means L-type tee, 9 means Y-type tee;
Sealing material code: B babbitt alloy, F fluorine rubber, F46 lining fluorine, H stainless steel, J rubber lining, M Monel alloy, N nylon plastic, Monel P, Y cemented carbide, W valve body directly processed;
Pressure rating code: 16 means the pressure is 16 kg (1.6Mpa) and the maximum can reach 64Mpa; 150LB means the American standard pound pressure, and the maximum pressure rating can reach 2500LB (150LB=1.6MPA/300LB=2.5-4.0mpa/400LB=6.4 mpa/600LB=10mpa); 5K means daily pressure, the maximum pressure is 63K;
Valve body material code: A titanium and titanium alloy, C carbon steel, I chromium molybdenum steel, P18-8 series stainless steel, RMo2Ti series stainless steel, S plastic.
Editing instructions for electric ball valve model:
VQ947F-16P Stainless steel electric flange V-shaped ball valve
1. V: indicates that the spool has a V-shaped structure
2. Q: represents the ball valve;
3. 9: indicates that the transmission mode is electric;
4. 4: The connection method is flange connection;
5. 7: The structure is a fixed straight flow channel;
6. F: The sealing material is fluorine rubber;
7. 16: Indicates that the nominal pressure is 1.6MPa;
8. P: indicates that the valve body is made of stainless steel.
More details for valve model establishment, you can visit another article: https://www.tanghaivalve.com/valve-model-establishment-and-meaning/
TH Valve is a professional manufacturer of butterfly valve, gate valve, check valve, globe valve, knife gate valve, ball valve with API, JIS, DIN standard, used in Oil, Gas, Marine industry, Water supply and drainage, fire fighting, shipbuilding, water treatment and other systems, with Nominal Diameter of DN50 to DN1200, NBR/EPDM/VITON, Certificates & Approvals: DNV-GL, Lloyds, DNV, BV, API, ABS, CCS. Standards: EN 593, API609, API6D













 © Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
© Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.