The difference of cryogenic valve and ordinary temperature valve
Cryogenic valves, as the name implies, are valves that can work in cryogenic and cryogenic conditions. The operating temperature is demarcated. Valves with operating temperatures below -40°C are usually called cryogenic valves, which are mainly used for gas liquefaction, For separation, transportation and storage equipment, the operating temperature can reach below -270℃. Currently, there are butterfly valves, check valves, gate valves, globe valves, ball valves, and throttle valves.
In recent years, ultra-low temperature valves have been used more and more widely, and they are one of the

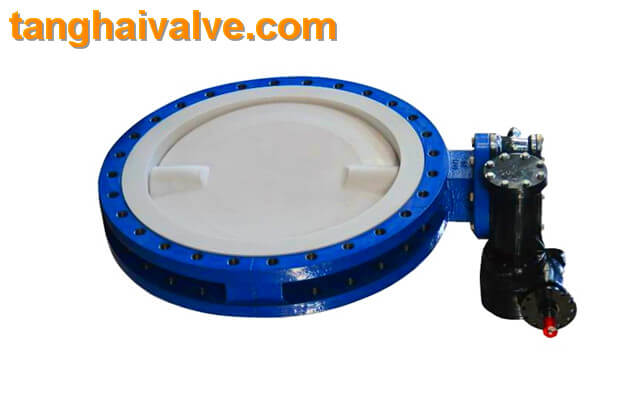
lug type butterfly valve, ductile iron, center lined,
indispensable important equipment in petrochemical, air separation, natural gas and other industries. The working medium is not only low in temperature, but most of them are toxic, or flammable and explosive. , And strong permeability, so it determines many special requirements for valve materials and design. It is not only required to work normally at the set temperature, but also to ensure the working performance at room temperature.
Compared with the normal temperature valve, the low temperature valve has a higher packing part and uses an extended stem. Its purpose is to reduce the heat transferred from the outside into the device; to ensure that the temperature of the stuffing box is above 0℃, so that the stuffing can work normally; to prevent the valve stem and the upper part of the valve cover at the stuffing box part from being too cold The parts are frosted or frozen.
The design of the long-neck bonnet is mainly the design of the neck length L. L refers to the distance from the bottom of the stuffing box to the upper surface of the upper sealing seat. It is related to the thermal conductivity of the material, the thermal conductivity area, the surface heat dissipation coefficient, and the heat dissipation area. , The calculation is relatively cumbersome, and it is generally obtained by experimental methods.
Ferritic stainless steel can be used when the temperature is higher than -100℃, austenitic stainless steel can be used when the temperature is lower than -100℃, copper alloy or aluminum alloy can be used for low pressure and small diameter valves, and the valve body should be able to withstand temperature changes sufficiently. The expansion and contraction, and the structure of the valve seat part will not be permanently deformed due to temperature changes.













 © Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
© Copyright 2020 Tianjin Tanghaidongyang Valve Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.